
Do pairwise alignments between all 7 sequences.Starting with a group of 7 globin-related sequences from different species.Length of the branch is used to determine which matrix to use and contributes to the alignment score.As the alignment proceeds in CLUSTALW the AA weight matrices are changed to more divergent scoring matrices.
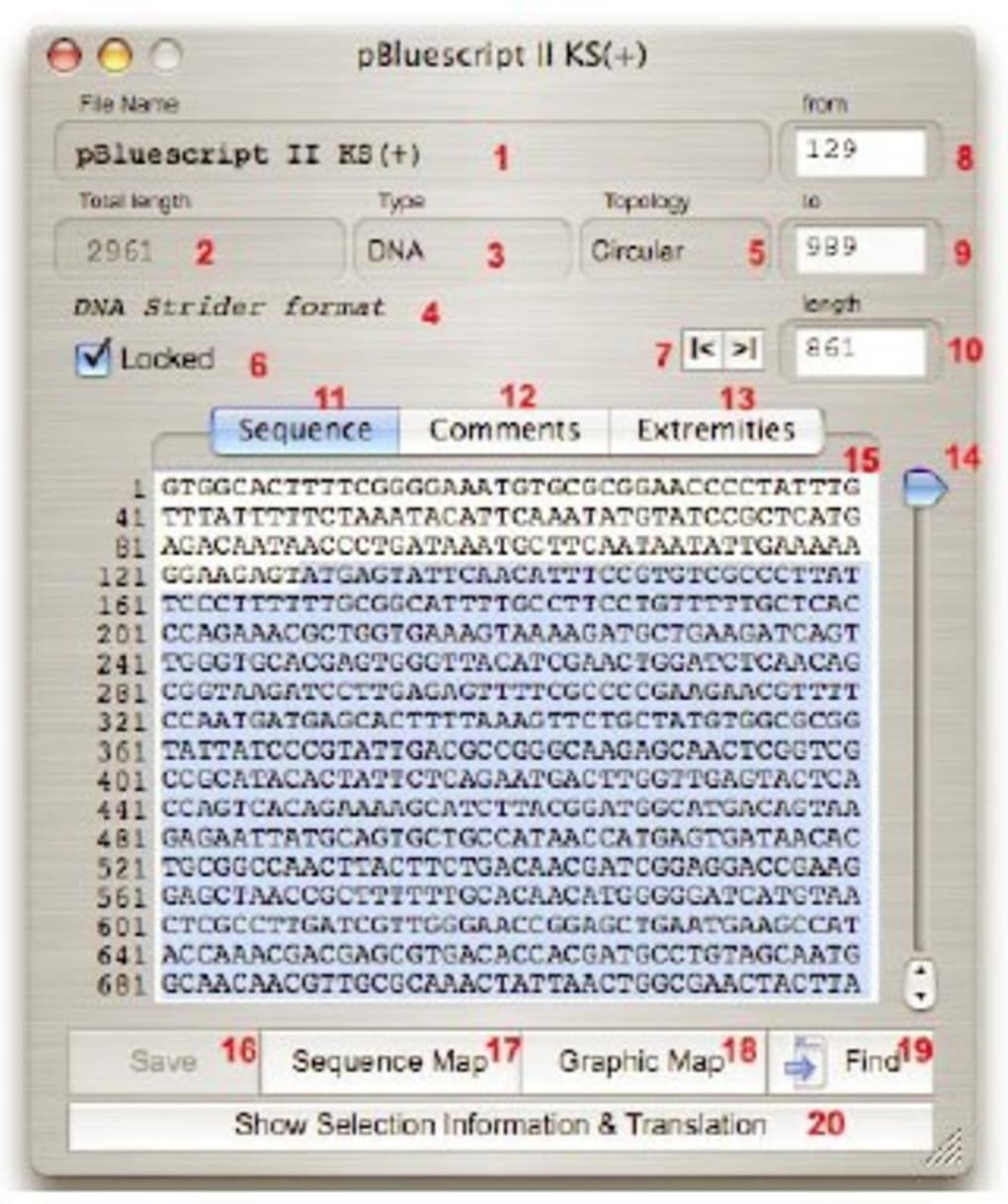
Macvector video series#
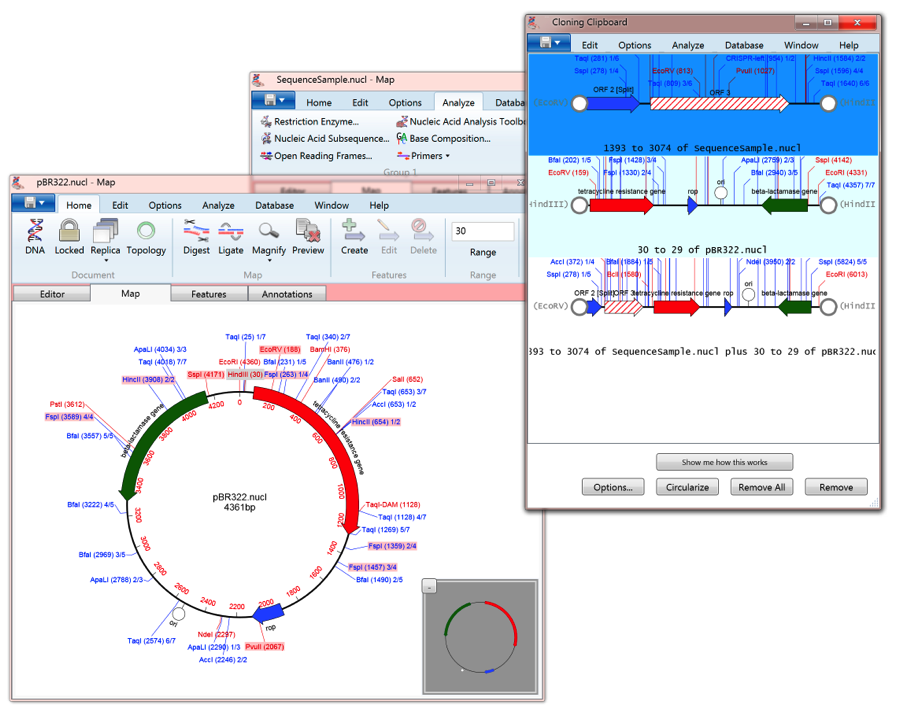
Step 2-Create Guide Tree Use the Distance Matrix to create a Guide Tree to determine the “order” of the sequences. Different sequences A B C In this distance matrix sequence A is 87% identical to sequence B
Thus, the higher the number the more closely related the two sequences are. 60 - Each number represents the number of exact matches divided by the sequence length (ignoring gaps). Step 1-pairwise alignments Compare each sequence with each other and calculate a distance matrix. Gaps that are introduced are never removed.Add sequences progressively in decreasing order of similarity.Align 2 most similar, then next 2 most similar.Create a guide tree of the most to least similar.Do a pair-wise comparison of all sequences.Command line & in Genious Pro, MacVector and MEGA5.Faster than CLUSTALW, especially on larger sequence sets.Can propagate errors made early in the alignment.Hierachical & progressive (NOT iterative).Global Iterative Alignments - Multiple re-building attempts to find best alignment (MUSCLE).Global Progressive Alignments - Match closely-related sequences first using a guide tree (CLUSTALW).Computationally expensive: Time grows as product of sequence lengths.Find alignment that maximizes a score function.Optimal Global Alignments -Dynamic programming.MSA is the starting point for phylogenetic analysis.Automated reconstruction of “contig” maps of genomic fragments such as ESTs.Allow us to search for other members of the family.Create “profiles” for protein families.Structure is more conserved than sequence.Use knowledge of structure of one or more members of a protein MSA to predict structure of other members.Similar genes are conserved across widely divergent species, often performing similar functions.Find out which parts “do the same thing” Best represents most likely evolutionary scenario.Hypothetical model of mutations (substitutions, insertions & deletions).Alignment of ≥ 3 sequences to bring as many similar characters into register as possible.Multiple Sequence AlignmentsAdvanced BLAST searches June 17, 2014


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
